Calls¶
Setting up, managing and making calls is the most important part of the FrontStage contact center. In this chapter you will find call instructions for agents, but most of the information is meant for their superiors (supervisors, shift managers, methodologists, etc.) and especially administrators and consultants who need to understand perfectly how call rules and distribution work and are set up.
For an overview of the mechanism for handling inbound and outbound calls, see the following diagram. The diagram shows the passage of inbound and outbound calls for the most common separated distribution queue.
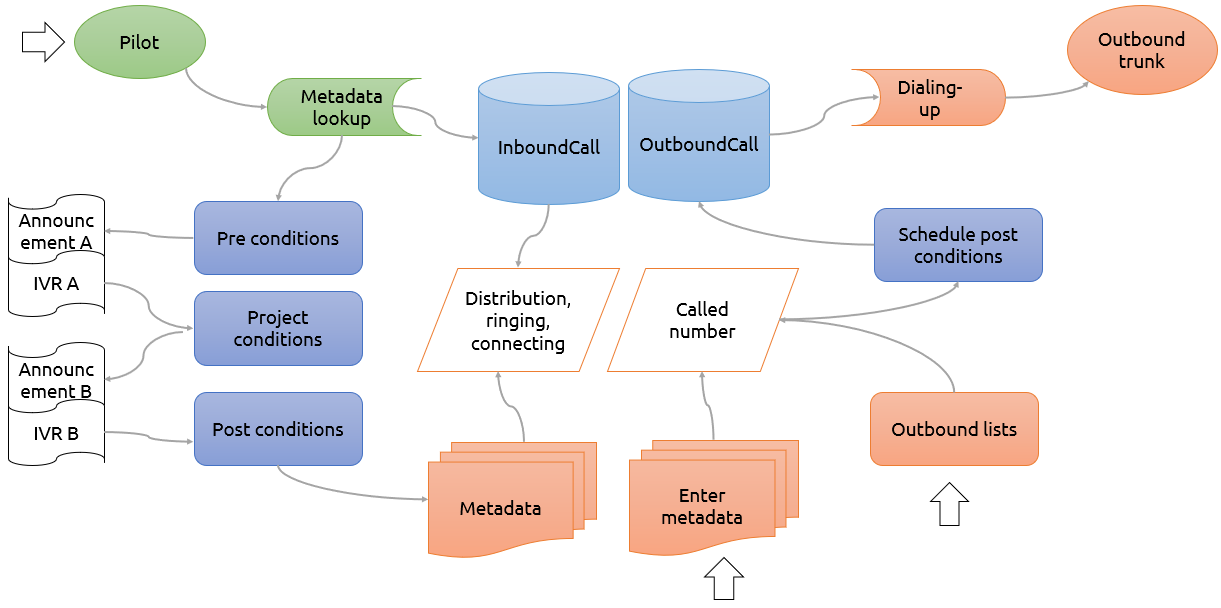
Inbound Calls
They always start on the PBX pilot.
After searching and finding the relevant metadata, a record is created in the
InboundCalltable.In parallel to creating a record in the database, the system gradually begins to evalute inbound, project and outbound rules (see below).
Once the call passes beyond the distribution rule (it was not terminated by one of the rules), then distribution to agents will begin with all the metadata added.
Routing inbound calls
Inbound calls pass through several types of rules.
Only one rule of each type is executed for each call.
The rule to be executed must meet certain limits. These are evaluated in a numerical order of the rules from the smallest order number. If its limits do not match, then the next rule in the sequence is tested. If you do not fill in any limit, it is not considered. If you fill in more limits, all of them must be met at the same time (AND operator).
If no matching rule is found, the processing is terminated (i.e. there must be at least one rule that “lets everything through” for each rule type).
A matching rule can perform certain actions and changes to the call metadata.
As soon as the call passes beyond the distribution rule (it was not terminated by one of the rules), it will be distributed to agents with all the metadata added.
If there are no free and suitable agents, the wait rule is searched for and the system then keeps waiting according to the rule.
Limits |
Actions |
Changes |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Pre conditions (more) |
address book; pilot; redirector; free IVR inputs less than; calendar |
play announcement |
language; language proficiency |
Project conditions (more) |
address book; pilot; redirector; calendar |
– |
priority; project; skill; preferred agent; language; proficiency |
Post conditions (more) |
logged-in agents less than; expected waiting time longer than; queue longer than; queue position greater than; current priority; current skill; current language; current proficiency; calendar; IVR mask, number of free IVR inputs |
play announcement |
priority; project; skill; language; proficiency; preferential/penalty time |
Wait post conditions (more) |
transferred; waiting time longer than; logged-in agents fewer than; expected waiting time longer than; queue length longer than; queue position greater than; current priority; current project; current skill; current language; current proficiency; pre-distributed; actual preferential time less than; IVR mask; number of free IVR inputs; calendar |
play announcement; run IVR script; end call; change the wait queue |
priority; target project; skill; target language; proficiency; cancel pre-distribution; shift of preferential time |
Outbound Calls
Outbound calls have two possible places of origin 1:
The agent needs to call someone and fill in the metadata of a future call (ad-hoc project call) via the user interface.
The second option is to create a call from campaigns (project call).
In both cases, at least the called party number and the project must be known.
Additional metadata, such as project or language, is added based on the matching scheduling rule or, if relevant, pre-distribution is cancelled or the call is terminated.
A call entry is created in the
OutboundCalltable.Call dialing and connecting begins.
Outbound rule routing
Outbound calls have only one type of rules - scheduling rules.
The principle of selecting and applying a rule is the same as for inbound calls.
Limits |
Actions |
Changes |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Schedule post conditions (more) |
waiting time longer than; registered agents less than; current priority; current project; current skill; current language; current proficiency; pre-distributed; calendar |
cancel pre-distribution; end call |
priority; project; skill; language; proficiency |
ServiceSync
ServiceSync is a key service for making calls that
Controls inbound and outbound calls
Logs in and out agents handling these calls
Footnotes
- 1
This means that private calls dialed directly on the phone are not managed by FrontStage.